Hey there! Let’s talk about inflammation. It’s a natural process that helps your body heal and defend itself from harm, but when it sticks around, it can lead to health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Inflammation occurs as a response to injury, infection, or illness, where your immune system releases chemicals that trigger an inflammatory response. This response includes redness, swelling, heat, and pain aimed at protecting the body. However, chronic inflammation can cause damage over time, contributing to various chronic diseases and negatively impacting your overall health and well-being.
The good news? You can adopt an anti-inflammation diet to combat this and boost your overall health.
This blog post is all about the knowledge and tips your need to adopt an anti-inflammation diet.
What Is an Anti-Inflammation Diet?
Simply put, an anti-inflammation diet is all about eating foods that reduce inflammation while avoiding those that trigger it. Think of it as focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and cutting back on processed, sugary, and fried stuff. This way, you support your body’s natural healing processes and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Key Components of an Anti-Inflammation Diet
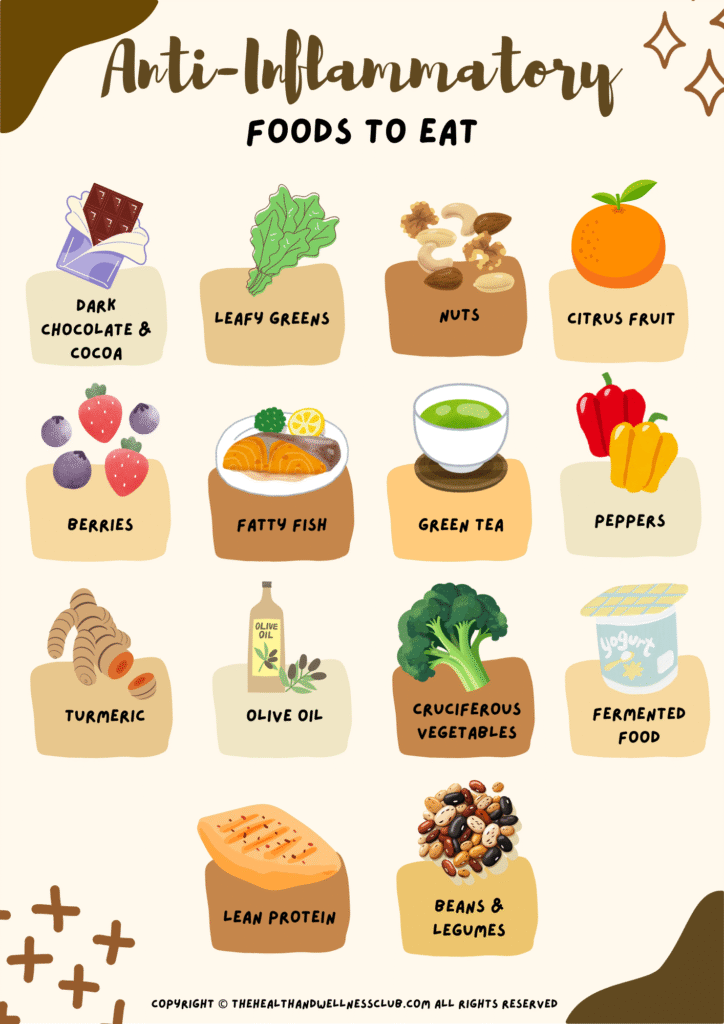
Let’s dive into the essentials. Here are the key components and the foods you should include:
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and veggies are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, minerals and fiber that help fight inflammation. Try to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to get a wide range of nutrients. Berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are superstars in this category.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are high in antioxidants called flavonoids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with vitamins A, C, and K, and other nutrients that reduce inflammation.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower contain sulforaphane, a compound that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, like those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, are crucial for reducing inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, are known for their anti-inflammatory benefits and can be found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, which help reduce inflammation.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, tuna, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which help fight inflammation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds provide healthy fats and other nutrients that support an anti-inflammatory diet.
Whole Grains
Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, are high in fiber and nutrients that help lower inflammation. Unlike refined grains, which can increase inflammation, whole grains retain their nutrient-rich bran and germ, making them a healthier choice.
- Quinoa: This ancient grain is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids, and is also high in fiber.
- Oats: Rich in beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber, oats help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
- Brown Rice: A whole grain that provides fiber, B vitamins, and minerals, brown rice is a nutritious alternative to white rice.
Lean Proteins
Including lean proteins in your diet can help reduce inflammation and provide essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. Opt for lean cuts of meat, poultry, and plant-based proteins like beans and legumes.
- Chicken Breast: A lean source of protein that provides essential amino acids without the added saturated fats found in red meat.
- Beans and Legumes: Black beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent plant-based protein sources that also provide fiber and other nutrients.
- Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based products are rich in protein and can be used in a variety of dishes as a meat substitute.
Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices not only add flavor to your meals but also contain powerful anti-inflammatory compounds. Turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon are some of the best options to include in your diet.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Adding turmeric to your dishes can help reduce inflammation.
- Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits, ginger can be used fresh, dried, or as a supplement.
- Garlic: Contains sulfur compounds that help reduce inflammation and boost the immune system.
- Cinnamon: This spice has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and can be added to both sweet and savory dishes.

Foods to Avoid
While embracing an anti-inflammation diet, it’s equally important to avoid foods that can trigger or exacerbate inflammation.
Processed and Sugary Foods
Processed foods, such as fast food, packaged snacks, and sweets, are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and preservatives that can increase inflammation. Limiting or avoiding these foods is crucial for reducing inflammation.
Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates, found in white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals, can cause spikes in blood sugar levels and promote inflammation. Opt for whole grains instead to keep your blood sugar stable and reduce inflammation.
Trans Fats & Fats High in Omega-6 Fats
The type of fats we consumed matters. In the Foods to Add section above, we have added “Good Fats” in the list, namely Omega-3 which is anti-inflammatory. We should avoid trans fats and vegetable oils that are high in omega-6 fats, which are pro-inflammatory. These processed vegetable oils include canola, soy bean, corn, safflower and cottonseed oil. Trans fats, commonly found in fried foods, margarine, and certain baked goods, are known to increase inflammation and should be avoided. Look for labels that state “partially hydrogenated oils” to identify trans fats in foods.These types of fats are commonly found in the processed or ultra-processed food, for instance, cookies, pastries, etc.

Creating an Anti-Inflammation Meal Plan
Now that you understand the key components of an anti-inflammation diet, let’s create a sample meal plan to help you get started.
Breakfast
Start your day with a nourishing breakfast that includes whole grains, healthy fats, and fruits.
- Smoothie: Blend spinach, frozen berries, avocado, banana, a tablespoon of hemp seeds and flaxseeds and vanilla extract for a nutrient-packed smoothie.
- Chia Seed Pudding: Combine chia seeds, almond milk, finely diced raspberries and hemp seeds. Let it sit overnight. In the next morning, add your favorite anti-inflammatory toppings like cacao nibs, berries, nuts and seeds.
Lunch
For lunch, focus on lean proteins, whole grains, and plenty of vegetables.
- Quinoa Salad: Mix cooked quinoa with chopped vegetables, like bell peppers, kale, tomatoes and cucumbers, and add a handful of chickpeas. Drizzle with olive oil and lemon juice, salt and pepper.
- Grilled Chicken Wrap: Fill a whole-grain wrap with grilled chicken, avocado, spinach, and a sprinkle of turmeric.
Dinner
End your day with a balanced dinner that includes healthy fats, lean proteins, and vegetables.
- Baked Salmon: Season a salmon fillet with garlic and dill, bake until cooked through, and serve with broccoli sauteed with garlic and cooked quinoa.
- Stir-Fry: Sauté tofu with a mix of colorful vegetables and a ginger-garlic sauce. Serve over brown rice.
Snacks
Choose anti-inflammatory snacks to keep you satisfied between meals.
- Fresh Fruit: Enjoy an apple, orange, or a handful of berries for a quick and healthy snack.
- Nuts and Seeds: A small handful of almonds or walnuts can provide a satisfying crunch and beneficial fats.
Adopting a Holistic Healthy Lifestyle
Apart from your diet, inflammation is also about your exercise, your lifestyle and the toxins around us. Consider to build a regular exercise routine and adding regular movement into your daily lives to counter inflammation. Stress and insomnia are other contributors to inflammation, so finding ways to destress and perfect our sleep are just as important as a good wholesome diet.
Let’s Wrap It Up
Adopting an anti-inflammation diet is a fantastic way to support your health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and avoiding processed and sugary items, you can help your body fight inflammation and promote overall wellness. Remember, you don’t need to be perfect; it’s all about making consistent, healthful choices that benefit your long-term health. Start incorporating these principles into your daily life and enjoy the journey towards a healthier, more vibrant you!